This is a post on the book that is important for my theoretical framework concerned with the contraints of risography – it is limited medium, however that can perhaps make us more creative, while working within it’s boundaries.
Constraints in Creativity: In Search of Creativity Science by Feiwel Kupferberg
Creativity is often imagined as limitless, a process of free expression unbound by rules. However, Constraints and Creativity by Feiwel Kupferberg challenges this idea by showing that constraints—whether physical, knowledge-based, or societal—are essential in shaping artistic innovation.
Constraints as a Driving Force
The book highlights how physical limitations, such as the materials available to artists, directly impact creative decisions. Greek architects, for example, designed slightly bulging columns to counteract optical illusions, showing how understanding constraints can enhance artistic outcomes. In painting, artists must evoke emotion in an instant, whereas novelists are constrained by time—forcing different creative approaches.
Knowledge constraints also shape artistic expression. While Greek painters rediscovered naturalistic forms, Egyptian artists intentionally abandoned them for symbolic reasons, reflecting their society’s reverence for the dead. These constraints—whether imposed by tradition, technology, or artistic intent—guide the evolution of creative practices.
Constraints in Printmaking and Risography
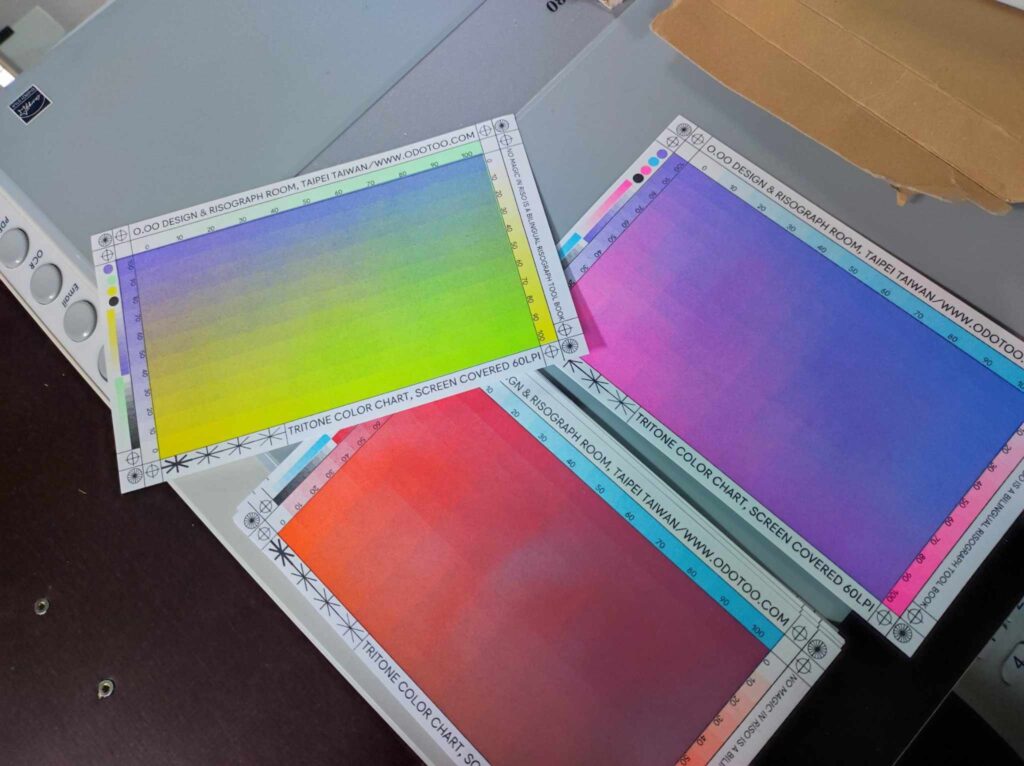
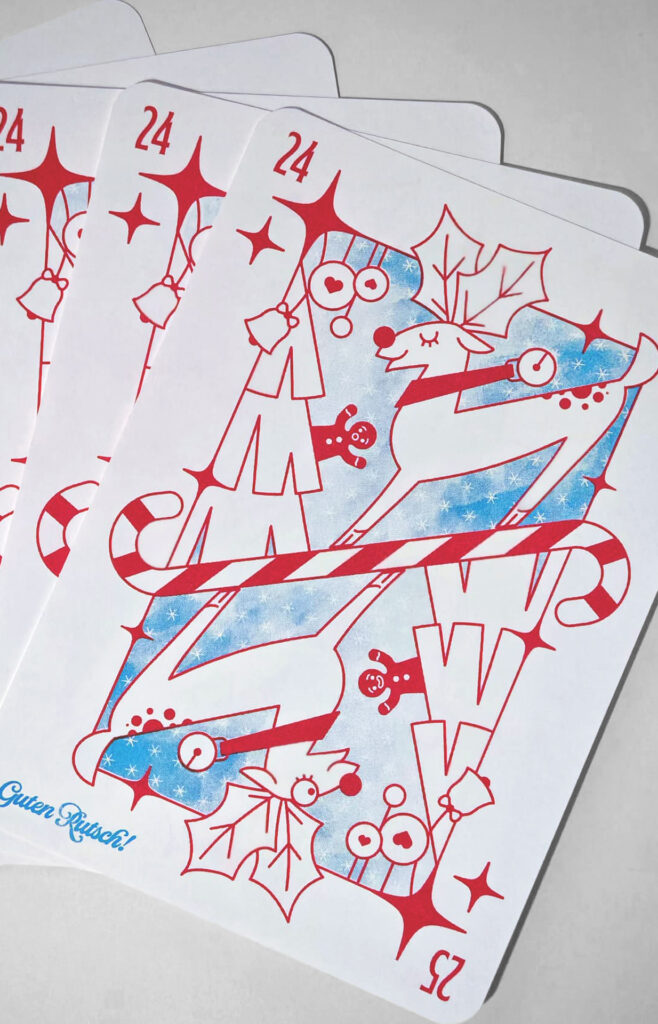
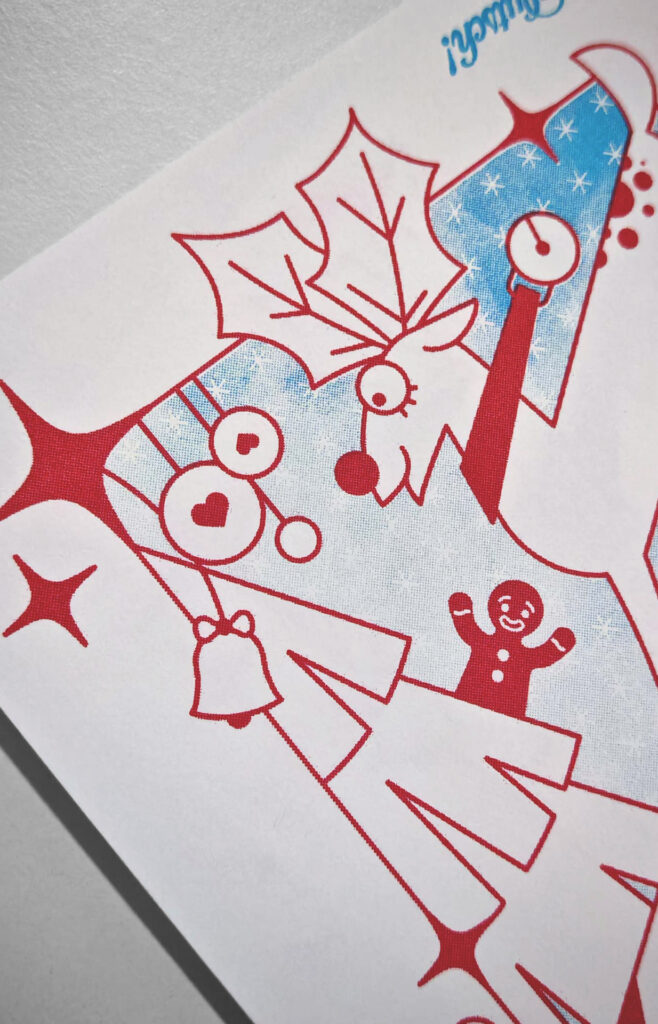
The principles from Kupferberg’s book can be applied to risography. The technique itself is bound by limitations: a limited color palette, the unpredictability of ink distribution, and mechanical constraints of the printer. Yet, these very challenges lead to unique textures, overlapping color effects, and unexpected results that digital printing cannot replicate. Artists working with risography learn to embrace these constraints, leading to distinctive and vibrant visual styles.
Creativity Within Limits
Rather than seeing constraints as obstacles, Kupferberg’s book suggests that they act as creative prompts. Whether in ancient architecture, modern literature, or risography, limitations force artists to develop innovative techniques, rethink their assumptions, and push the boundaries of their craft.