When we think about climate change, our minds often conjure images of industrial smokestacks and exhaust-spewing vehicles. It’s instinctive to link climate issues with carbon emissions, but this singular focus is what Dr. Jan Konietzko from COGNIZANT termed as „Carbon Tunnel Vision.“
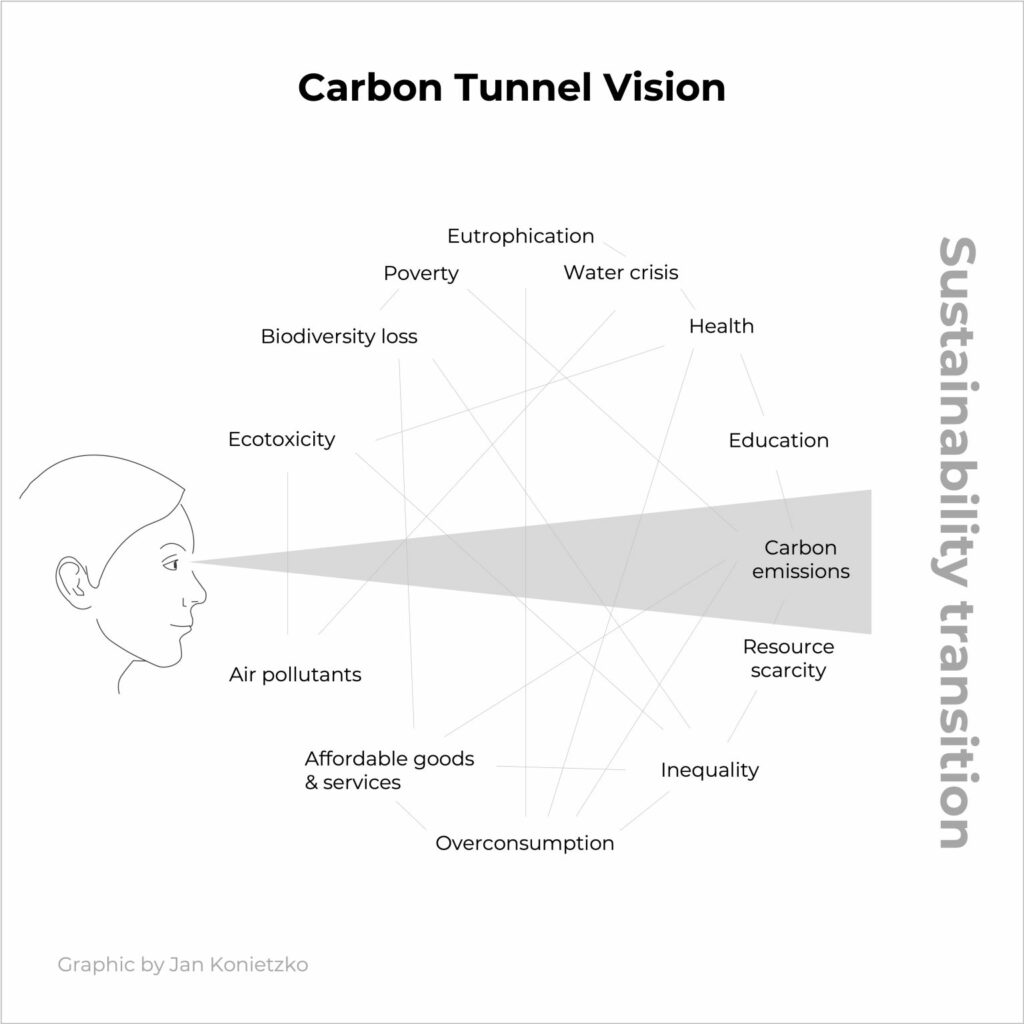
What exactly does this entail? It means getting fixated solely on carbon emissions while ignoring the broader spectrum of sustainability challenges. This tunnel vision can blind organizations to crucial aspects vital for combating climate change and fostering sustainability.
Carbon Tunnel Vision in Digital Sustainability
In the realm of digital sustainability, „Carbon Tunnel Vision“ refers to the tendency to narrowly focus solely on reducing carbon emissions while neglecting other critical environmental and social impacts in digital operations and technologies. Just as in traditional sustainability approaches, where organizations may prioritize carbon emissions reduction without considering broader sustainability goals, digital sustainability can suffer from this tunnel vision.
For instance, in digital infrastructure and operations, efforts may primarily revolve around minimizing energy consumption and transitioning to renewable energy sources to reduce carbon footprints. While reducing carbon emissions is crucial, a narrow focus on this aspect alone overlooks other significant environmental and social impacts associated with digital technologies, such as:
E-Waste Management
The rapid turnover of electronic devices and equipment leads to substantial electronic waste (e-waste) generation, posing environmental and health hazards if not managed properly.
Supply Chain Transparency
Ensuring transparency and sustainability across the supply chain for digital hardware components (e.g., rare earth metals, minerals) is essential to address issues like resource depletion, unethical mining practices, and human rights violations.
Digital Inclusion
Digital sustainability should also encompass efforts to bridge the digital divide and ensure equitable access to technology and digital resources, addressing social disparities and promoting inclusivity.
Data Privacy and Security
Protecting user data and ensuring cybersecurity in digital platforms are crucial aspects of sustainability, safeguarding individuals‘ rights and preventing environmental harm from data breaches or misuse.
Ethical AI and Automation
Considering the ethical implications of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation technologies is vital to prevent biases, discrimination, and social injustices in digital systems and decision-making processes.
By expanding the scope of digital sustainability beyond carbon emissions reduction and adopting a more holistic approach, organizations can address these multifaceted challenges and strive for sustainable digital transformation that benefits both the environment and society as a whole.
- Dr. Konietzko, Jan (2022): Moving beyond carbon tunnel vision with a sustainability data strategy.
URL: https://www.cognizant.com/us/en/insights/insights-blog/moving-beyond-carbon-tunnel-vision-with-a-sustainability-data-strategy-codex7121 ↩︎